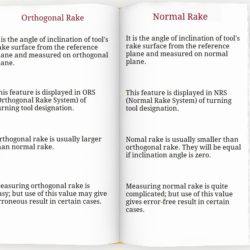
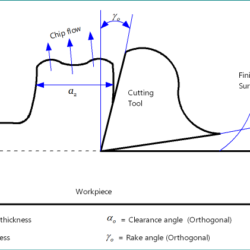
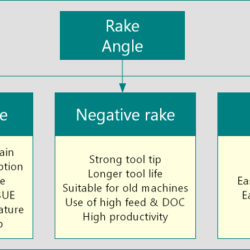
Difference Between ORS System and NRS System of Tool Designation
Machining or metal cutting is one type of subtractive manufacturing process where excess material is gradually removed from the preformed blank to produce desired three dimensional feature or product. Conventional machining processes (like straight turning, taper turning, internal turning, threading, facing, drilling, boring, reaming, tapping, planing, shaping, slotting, milling, fly cutting, hobbing, grooving, parting, etc.) utilize a sharp wedge shaped cutting tool (cutter) to remove unwanted material. This cutter compresses